新闻动态 News
查看更多 >>
-
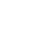
2023-02-282023年2月23日,望石智慧研究团队助力中国科学院物理所姜道华研究员在Nature Communications期刊发表了题为:Structure of human NaV1.6 channel reveals Na+ selectivity and pore blockade by 4,9-anhydro-tetrodotoxin的研究论文。(文章链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-36766-9) 该研究解析了人 NaV1.6/β1/β2和与胍盐神经毒素 4,9-脱水河豚毒素 (4,9-ah-TTX) 复合的冷冻电镜结构,并利用基于实验密度图的NCI(非共价键相互作用)指纹分析和分子动力学技术深入分析了小分子与蛋白的作用模式,为从分子机制层面揭示阻断剂抑制NaV1.6以及对不同钠通道选择性提供了有力支撑。 钠通道在中枢和周围神经系统的神经元中广泛表达,在调节神经元兴奋性方面起着关键作用。钠通道的功能障碍与癫痫性脑病、智力障碍和运动障碍有关,也是治疗这些疾病重要的药物靶点。目前虽然在临床上已经成功实现通过钠通道的抑制来控制在慢性疼痛、癫痫和心律失常等多种情况下发生的病理性放电,但是第一代钠通道调节剂药物对亚型选择性较低,因...
-
2022-10-099月28日上午,北京大学举行了校企联合研发平台集体签约仪式(北大医学办学 110 周年系列活动),北大医学——望石智慧AI生物医药数据技术协同创新联合实验室正式挂牌。北京大学常务副校长兼任医学部主任乔杰院士、医学部副主任肖源、产业办副主任沈娟、药学院研究员刘振明和望石智慧首席运营官项雪女士出席了该会议。 此次共建联合实验室的合作方为刘振明教授团队及北京大学药物设计、信息与情报分析中心。望石智慧一直致力于AI制药基础理论突破和技术落地,挂牌后,双方将在AI制药领域进行高层次人才的联合培养、承担国家重大科研任务、并对产业界关注的前瞻性课题进行联合攻关,以加速赋能更快、更好的新药研发! 北大医学——望石智慧AI生物医药数据技术协同创新联合实验室期待国际顶尖研发人员的加入! 关于刘振明团队及北京大学药物设计、信息与情报分析中心 该团队隶属于北京大学创新药物研究院,专门从事原研药物研究和情报支撑,专注于生物医药研发领域的集创新信息、数据服务和技术咨询、提供结构化药物研发大数据...
-
2022-08-228月18日,致力于建立更快、更好药物研发新范式的望石智慧,凭借其在交叉学科管理体系优化和AI制药底层理论的创新脱颖而出,荣获《哈佛商业评论》“高能创新团队奖”。一同获奖的还有华为、腾讯、默克和拜耳等28家优秀企业, 望石智慧是获得该奖项唯一的AI制药公司。 交叉学科管理体系优化 AI工具介入药物研发,需要大量跨学科问题定义、应用开发以及数据和工具使用,企业内学科交叉的复杂程度和沟通难度远高于传统医药行业。望石智慧搭建了独特的“多/跨学科培训”以及“跨领域项目管理的沟通制度”等支撑体系,使药物研发问题能迅速、清晰地被定义为AI问题,贴近药物研发的真实需求。跨学科专业团队构建能够在应用技术落地的同时,快速推动底层基础理论的探索。 AI制药底层基础理论的创新 AI制药新范式的形成,需要挑战的底层问题与传统药物研发有所不同。望石智慧从成立起,就依托交叉学科的管理体系,探索AI制药的底层问题。分子表征是其中一个重要方向,望石智慧在世界范围内首次创造性的把晶体...
-
2022-07-18近日,翰森制药集团有限公司(股票:3692.HK)(“翰森制药”)和北京望石智慧科技有限公司(“望石智慧”)宣布,双方继2021年7月首次合作之后,进一步扩大在AI赋能药物早期研发领域的战略合作关系。 根据协议,望石智慧将基于AI赋能的药物分子设计平台与产业经验丰富的复合型药物研发团队,将靶点口袋研究、分子生成、超高通量筛选、化合物与靶标蛋白的精准结合能计算等多个技术模块高度整合,助力新药早期研发提效提速,降低成本和提高成功率。 作为中国领先的创新驱动型制药公司,翰森制药在自主研发与全球业务拓展双轮驱动战略下,不断整合优势资源,打造出具有国际先进水平的研发体系和创新平台。公司以全球化视野,加速AI赋能,以期为更多临床未竟的医疗需求进行更广阔更前沿的多元探索,不断推出具有巨大潜力的诊疗手段和创新药物。 望石智慧旨在携手翰森制药,进一步释放AI平台的技术能力,加速AI和医药产业的深度结合,共同打造出更多具有全球竞争力的产品管线,让更多高质量好药早日造福全球患者。 关于翰森制药 翰...
-
2022-04-27AI究竟应该从什么样的角度赋能一个行业?毫无疑问,是该行业特有的数据。 那么,制药领域特有的、行业级别的数据是什么,AI又应该如何以最佳姿态切入? 望石研究团队历时3年,充分融合结构生物学和AI的基础理论,提出了一整套以大分子实验电子密度为数据基础的AIDD技术体系,涵盖了基于靶点口袋的3D分子生成技术和基于高精度能量计算的高效筛选体系。 继该技术体系的轮廓于去年ACS Fall 2021以大会报告的形式亮相后,望石研究团队又以研究论文的形式发表了部分数据基础,以期在行业层面推动AIDD的整体发展。该研究成果于2022年4月11在JCIM以副封面形式发表。(论文链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jcim.1c01406) 望石的整体技术体系将会逐步以更多原创成果的形式发布,敬请期待!同时,望石也期待与学术界和工业界同仁开展讨论和合作。 关于JCIM: Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (J. Chem. Inf. Model., JCIM)是美国化学会旗下,专注于化学信息学和计算模拟研究的顶级期刊之一。...
-
2022-04-27文献或专利的检索一直是医药研发人员工作中重要的环节,目前主流的检索是基于文本信息本身,或者通过挖掘文献内容推荐实体之间关系,来实现其目标。显然,一个或数个关键词的信息是不足以涵盖整篇文本的全部含义,这会导致检索到大量不相关论文,而图片信息量大、独特性高,可能是更好的选择之一。早期医药研发中,医药研发人员也需要搜索文献或专利中关键的化学结构式信息(图片或图表等形式),因此,快速且精准的搜索到包含相同或相似图片信息(化学分子式)的文献或专利是行业急需的。 近期,北京大学王选计算机研究所的吕肖庆团队主导,联合望石智慧及其他学术机构,开发了D2D-MR模型(Document-to-document Recommender System for Medical Literature)很好的解决了该问题,相关成果被IEEE发表(论文链接:Doc-to-Doc Recommender for Medical Literature with Similarity of Molecule Graphs | IEEE Conference Publication | IEEE Xplore),这也是该团队之前分子检索工作的延伸。模型包括PDF分析、分子图提取、分子相似性...
学术进展 Academic Progress
查看更多 >>
-
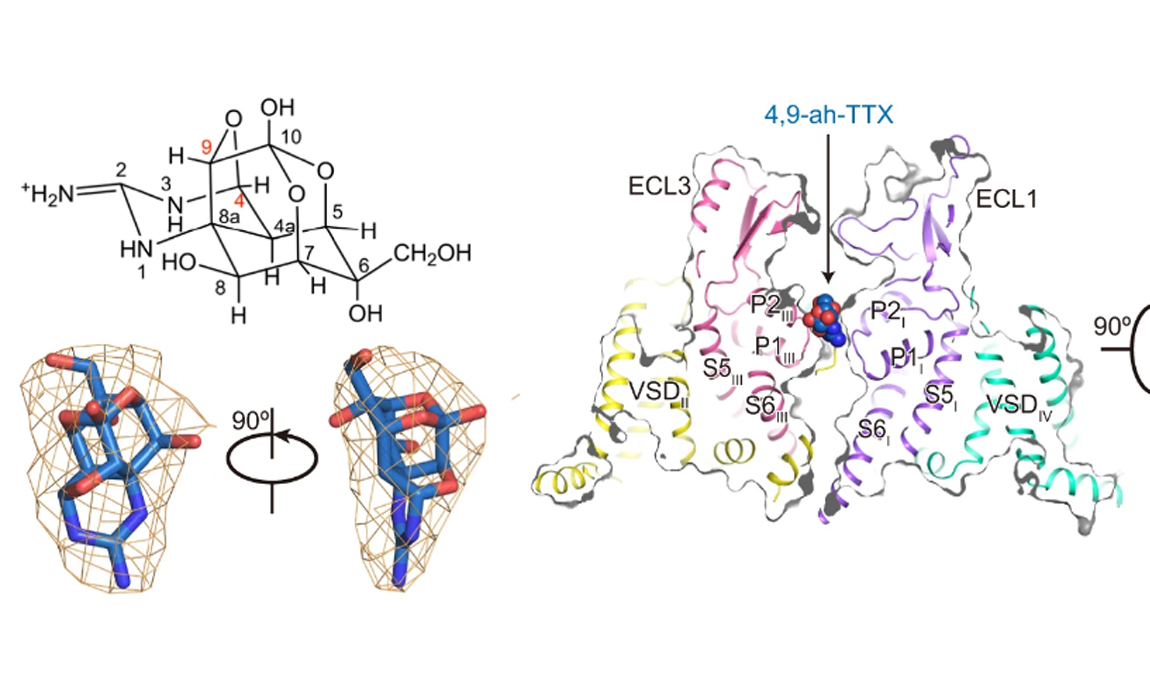
2024-07-11Weiqiang Fu, Yujie Mo, Yi Xiao, Chang Liu, Feng Zhou, Yang Wang, Jielong Zhou*, Yingsheng J. Zhang DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.3c01181 Abstract: Exclusively prioritizing the precision of energy prediction frequently proves inadequate in satisfying multifaceted requirements. A heightened focus is warranted on assessing the rationality of potential energy curves predicted by machine learning-based force fields (MLFFs), alongside evaluating the pragmatic utility of these MLFFs. This study introduces SWANI, an optimized neural network potential stemming from the ANI framework. Through the incorporation of supplementary physical constraints, SWANI aligns more cohesively with chemical expectations, yielding rational potential energy profiles. It also exhibits superior predictive precision compared with that of the ANI model. Addition...
-
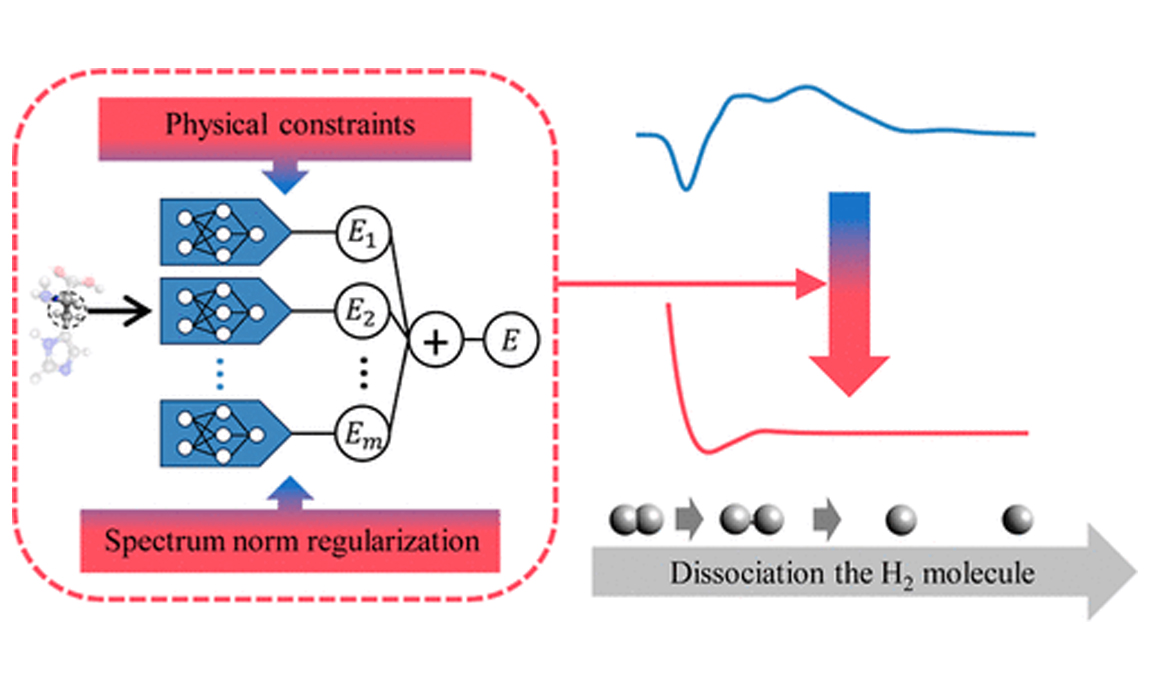
2023-12-11Di Wu, Qihao Chen, Zhuoya Yu, Bo Huang, Jun Zhao, Yuhang Wang, Jiawei Su, Feng Zhou, Rui Yan, Na Li, Yan Zhao & Daohua Jiang DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06926-4 Abstract: Vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) accumulates monoamines in presynaptic vesicles for storage and exocytotic release, and has a vital role in monoaminergic neurotransmission1,2,3. Dysfunction of monoaminergic systems causes many neurological and psychiatric disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, hyperkinetic movement disorders and depression4,5,6. Suppressing VMAT2 with reserpine and tetrabenazine alleviates symptoms of hypertension and Huntington’s disease7,8, respectively. Here we describe cryo-electron microscopy structures of human VMAT2 complexed with serotonin and three clinical drugs at 3.5–2.8 Å, demonstrating...
-
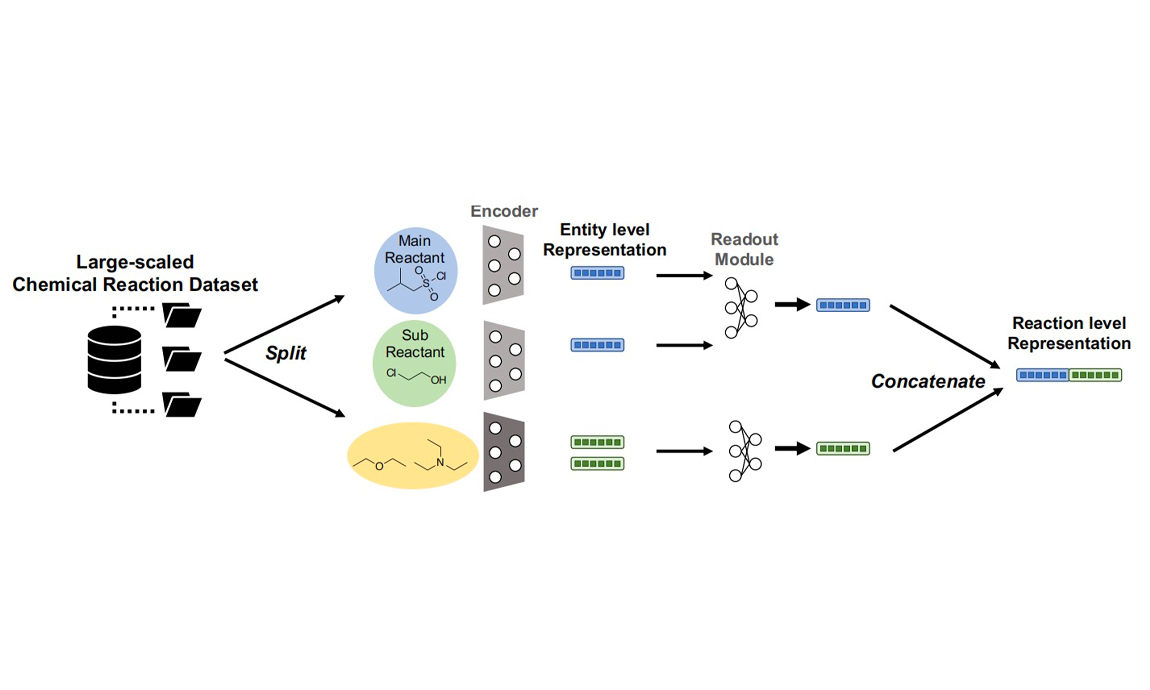
2023-12-05Bo Qiang, Yiran Zhou, Yuheng Ding, Ningfeng Liu, Song Song, Liangren Zhang, Bo Huang & Zhenming Liu DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-023-00764-9 Abstract: Chemical reactions are the fundamental building blocks of drug design and organic chemistry research. In recent years, there has been a growing need for a large-scale deep-learning framework that can efficiently capture the basic rules of chemical reactions. In this paper, we have proposed a unified framework that addresses both the reaction-representation learning and molecule generation tasks, which allows for a more holistic approach. Inspired by the organic chemistry mechanism, we develop a new pretraining framework that enables us to incorporate inductive biases into the model. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art results in performance of challenging downstream tasks. By possessing chemical kno...
-
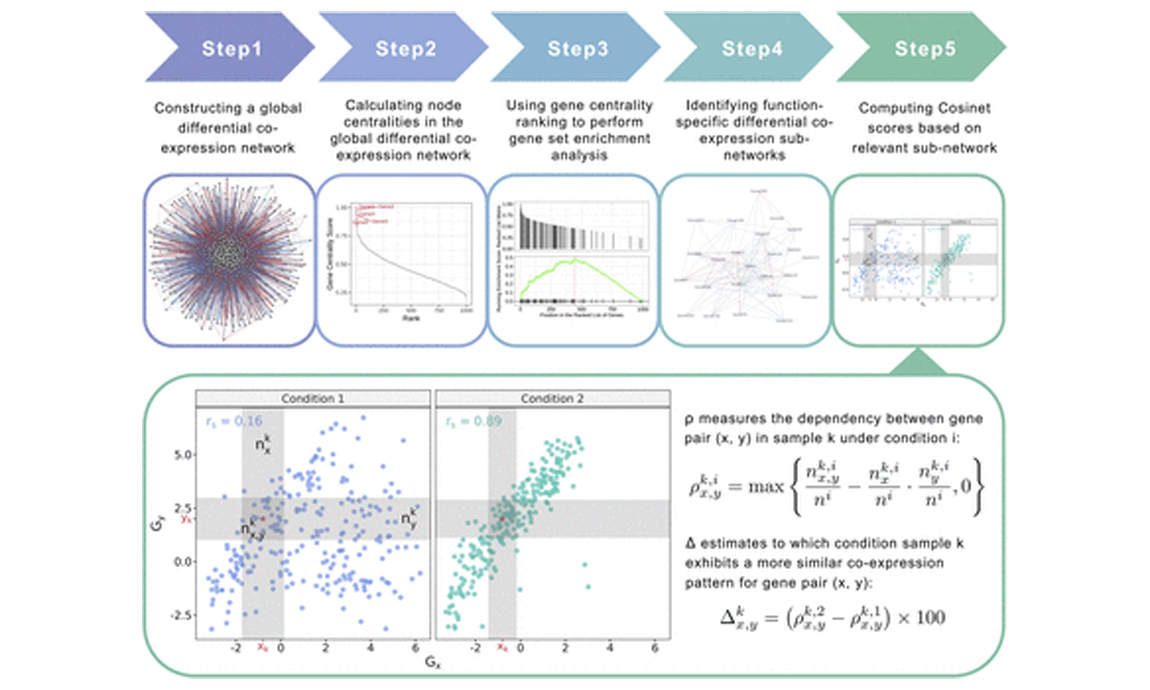
2023-11-21Lanying Wei, Yucui Xin,Mengchen Pu,Yingsheng Zhang DOI: https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.202302253 Abstract: To effectively understand the underlying mechanisms of disease and inform the development of personalized therapies, it is critical to harness the power of differential co-expression (DCE) network analysis. Despite the promise of DCE network analysis in precision medicine, current approaches have a major limitation: they measure an average differential network across multiple samples, which means the specific etiology of individual patients is often overlooked. To address this, we present Cosinet, a DCE-based single-sample network rewiring degree quantification tool. By analyzing two breast cancer datasets, we demonstrate that Cosinet can identify important differences in gene co-expression patterns between individual patients and generate scores for each in...
-
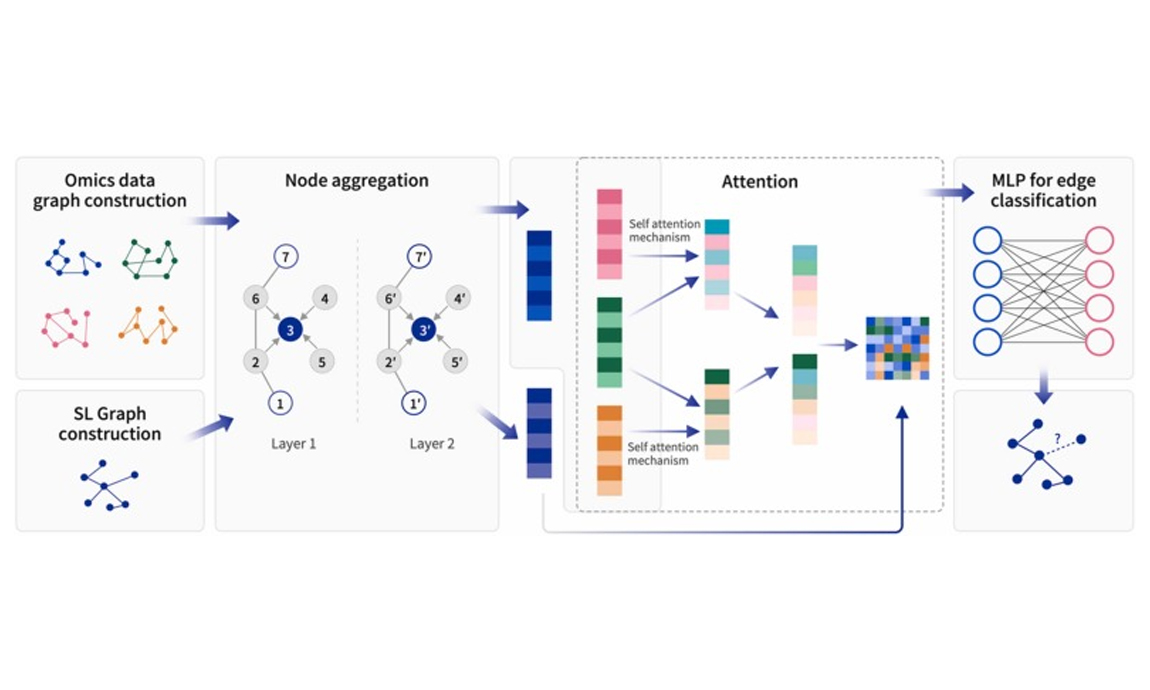
2023-10-09Mengchen Pu , Kaiyang Cheng, Xiaorong Li , Yucui Xin, Lanying Wei, Sutong Jin, Weisheng Zheng, Gongxin Peng, Qihong Tang, Jielong Zhou, Yingsheng Zhang DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2023.10.011 Abstract: Synthetic lethal (SL) pairs are pairs of genes whose simultaneous loss-of-function results in cell death, while a damaging mutation of either gene alone does not affect the cell’s survival. This makes SL pairs attractive targets for precision cancer therapies, as targeting the unimpaired gene of the SL pair can selectively kill cancer cells that already harbor the impaired gene. Limited by the difficulty of finding true SL pairs, especially on specific cell types, current computational approaches provide only limited insights because of overlooking the crucial aspects of cellular context dependency and mechanistic understanding of SL pai...
-
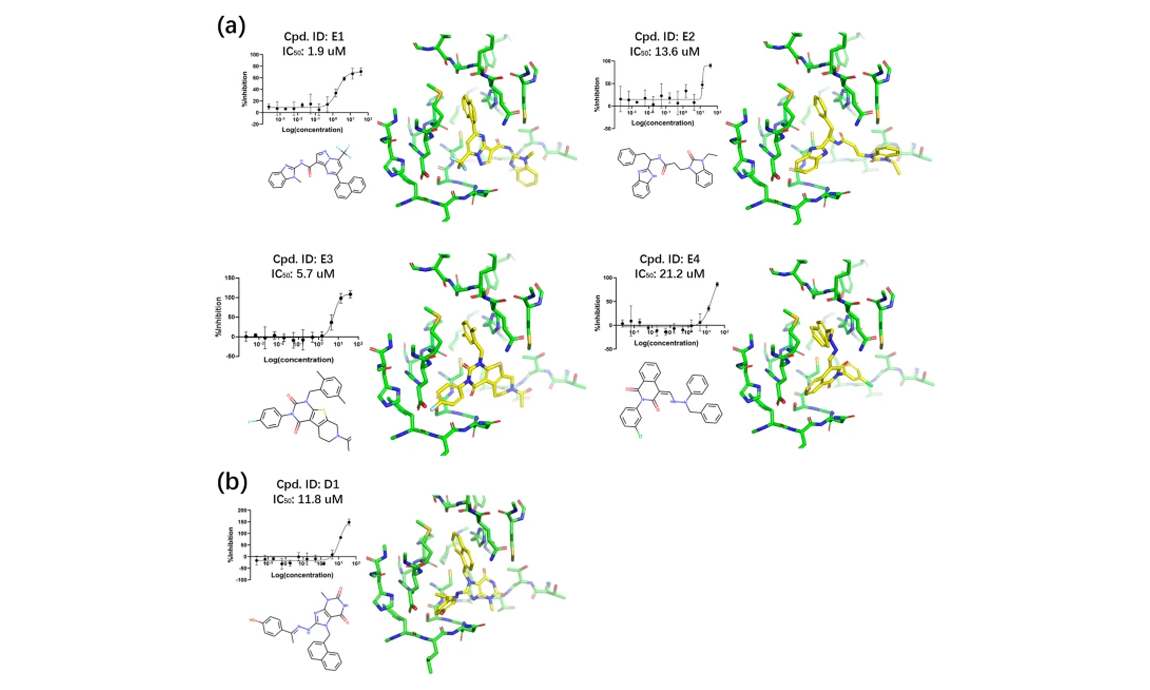
2023-08-23Wenzhi Ma, Yuan Le, Xiaoxuan Shi, Qingbo Xu, Yang Xiao, Yueying Dou, Xiaoman Wang, Wenbiao Zhou, Hongbo Zhang, Bo Huang DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-023-00984-5 Abstract: The quest for effective virtual screening algorithms is hindered by the scarcity of training data, calling for innovative approaches. This study presents the use of experimental electron density (ED) data for improving active compound enrichment in virtual screening, supported by ED’s ability to reflect the time-averaged behavior of ligands and solvents in the binding pocket. Experimental ED-based grid matching score (ExptGMS) was developed to score compounds by measuring the degree of matching between their binding conformations and a series of multi-resolution experimental ED grids. The efficiency of ExptGMS was validated using both in silico tests with the Dir...